
Sodium is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metallic, being in grouping 1 of the periodic table, because it has a single electron in its outer beat that it readily donates, creating a positively charged cantlet—the Na+ cation.
Metallic sodium is used mainly for the production of sodium borohydride, sodium azide, indigo, and triphenylphosphine. Employed only in rather specialized applications, merely about 100,000 tonnes of metal sodium are produced annually. Sodium is now produced commercially through the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride.
Protons and Neutrons in Sodium
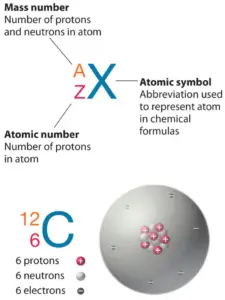 Sodium is a element with atomic number11 which means at that place are 11 protons in its nucleus. Full number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electrical accuse of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (unproblematic charge) equals to1,602 ten 10-xix coulombs.
Sodium is a element with atomic number11 which means at that place are 11 protons in its nucleus. Full number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electrical accuse of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (unproblematic charge) equals to1,602 ten 10-xix coulombs.
The full number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is chosen theneutron number of the atom and is given thesymbol North. Neutron number plus atomic number equals diminutive mass number:N+Z=A. The divergence between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as theneutron backlog: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, there is unremarkably a variety of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same diminutive number and are therefore the same chemical element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Sodium are23.
Chief Isotopes of Sodium
Its only stable isotope is23Na. Two radioactive, cosmogenic isotopes are the byproduct of cosmic ray spallation: 22Na has a one-half-life of 2.6 years and 24Na, a half-life of 15 hours; all other isotopes have a half-life of less than 1 minute.
Sodium-23 is composed of 11 protons, 12 neutrons, and 11 electrons. Astute neutron radiation exposure (e.g., from a nuclear criticality blow) converts some of the stable 23Na in human claret plasma to 24
Na. By measuring the concentration of this isotope, the neutron radiation dosage to the victim can be computed.
Sodium-22 is composed of 11 protons, 11 neutrons, and 11 electrons. odium-22 is a radioactive isotope of sodium, undergoing positron emission to 22Ne with a half-life of 2.605 years. It is likewise normally used as a positron source in positron annihilation spectroscopy.
Sodium-24 is composed of 11 protons, 12 neutrons, and xi electrons. Sodium-24 is i of the near important isotopes. Information technology is radioactive and created from mutual sodium-23 by neutron bombardment. Therefore its action accounts for most of the reactor coolants activity when reactor is at total power.
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Sodium is 11. Each electron is influenced by the electrical fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the cantlet.
Since the number of electrons and their organisation are responsible for the chemical beliefs of atoms, thediminutive number identifies the diverse chemic elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element's electron shells, particularly the outermost valence vanquish, is the chief factor in determining its chemical bonding beliefs. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Electron configuration ofSodiumis[Ne] 3s1.
Possible oxidation states are-1; +1.
Sodium atoms take 11 electrons, one more than the stable configuration of the noble gas neon. Sodium normally forms ionic compounds involving the Na+ cation. Sodium is unremarkably quite reactive with air, and the reactivity is a function of the relative humidity, or water-vapour content of the air. The corrosion of solid sodium by oxygen too is accelerated by the presence of pocket-size amounts of impurities in the sodium. In ordinary air, sodium metal reacts to form a sodium hydroxide film, which tin can rapidly blot carbon dioxide from the air, forming sodium bicarbonate.
Sodium metal can exist easily cut with a pocketknife and is a skillful conductor of electricity and rut because information technology has only one electron in its valence shell, resulting in weak metallic bonding and free electrons, which acquit free energy.
Most Common Chemical compound of Sodium
Salt is generally sodium chloride, the ionic compound with the formula NaCl, representing equal proportions of sodium and chlorine. Ocean salt and freshly mined salt (much of which is sea table salt from prehistoric seas) also contain small amounts of trace elements (which in these pocket-size amounts are generally good for institute and beast health.
About Protons
 A proton is 1 of the subatomic particles that make upwardly matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upabout half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to 1.67262 × ten−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron simply nigh 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean foursquare radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 yard, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
A proton is 1 of the subatomic particles that make upwardly matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upabout half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to 1.67262 × ten−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron simply nigh 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean foursquare radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 yard, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
The protons exist in the nuclei of typical atoms, along with their neutral counterparts, the neutrons. Neutrons and protons, commonly callednucleons, are bound together in the diminutive nucleus, where they account for 99.ix percent of the atom's mass. Research in high-energy particle physics in the 20th century revealed that neither the neutron nor the protonis non the smallest edifice block of matter.
Well-nigh Neutrons
A neutron is one of the subatomic particles that make up matter. In the universe, neutrons are abundant, making upmore than half of all visible thing. It hasno electric charge and a residuum mass equal to 1.67493 × x−27 kg—marginally greater than that of the proton but nearly 1839 times greater than that of the electron. The neutron has a hateful square radius of about 0.viii×x−15 m, or 0.viii fm, and it is a spin-½ fermion.
Atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which concenter each other throughthe nuclear force, while protons repel each other viathe electrical force due to their positive charge. These two forces compete, leading to various stability of nuclei. There are only certain combinations of neutrons and protons, which formsstable nuclei.
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, considering they attract each other and protons , which helps commencement the electrical repulsion between protons. As a effect, as the number of protons increases,an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to class a stable nucleus. If there are too many or too few neutrons for a given number of protons, the resulting nucleus is not stable and information technology undergoes radioactive decay.Unstable isotopesdecay through various radioactive decay pathways, virtually ordinarily alpha disuse, beta decay, or electron capture. Many other rare types of decay, such every bit spontaneous fission or neutron emission are known. It should exist noted that all of these disuse pathways may be accompanied bythe subsequent emission of gamma radiation. Pure alpha or beta decays are very rare.
Virtually Electrons and Electron Configuration
The periodic tabular array is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the ground of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical construction) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Cognition of theelectron configuration of dissimilar atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic tabular array of elements.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Thechemical properties of the cantlet are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number andsystem of electrons. Theconfiguration of these electrons follows from the principles of breakthrough mechanics. The number of electrons in each element'south electron shells, particularly the outermost valence vanquish, is the main factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic tabular array, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Information technology is thePauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy dissimilar energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom's electrons has been assigned a unique set of breakthrough numbers. This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements.
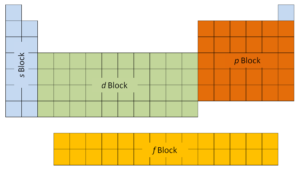 The offset 2 columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thesouthward subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the outset two rows of the periodic table are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep blockare the right-about 6 columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-cavalcade department that is ordinarily depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic tabular array. It could be part of the principal torso, just and so the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
The offset 2 columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thesouthward subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the outset two rows of the periodic table are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep blockare the right-about 6 columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-cavalcade department that is ordinarily depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic tabular array. It could be part of the principal torso, just and so the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and and so an abbreviated notation is used. The electron configuration can exist visualized as the core electrons, equivalent to thenoble gas of the preceding period, and the valence electrons (e.g. [Xe] 6s2 for barium).
Oxidation States
Oxidation states are typically represented by integers which may exist positive, zero, or negative. Nigh elements take more than one possible oxidation state. For example, carbon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +four.
The current IUPAC Gold Book definition of oxidation state is:
"Oxidation state of an atom is the charge of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds…"
and the term oxidation number is nearly synonymous. An chemical element that is non combined with any other unlike elements has an oxidation land of 0. Oxidation state 0 occurs for all elements – it is simply the element in its elemental form. An atom of an element in a compound will have a positive oxidation state if information technology has had electrons removed. Similarly, calculation electrons results in a negative oxidation state. We have also distinguish between the possible and common oxidation states of every element. For example, silicon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +four, simply merely -4, 0 and +4 are mutual oxidation states.
Summary
| Chemical element | Sodium |
| Number of protons | eleven |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 23 |
| Number of electrons | xi |
| Electron configuration | [Ne] 3s1 |
| Oxidation states | -1; +1 |

Source: www.luciteria.com
Other backdrop of Sodium

 Sodium is a element with atomic number11 which means at that place are 11 protons in its nucleus. Full number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electrical accuse of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (unproblematic charge) equals to1,602 ten 10-xix coulombs.
Sodium is a element with atomic number11 which means at that place are 11 protons in its nucleus. Full number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electrical accuse of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (unproblematic charge) equals to1,602 ten 10-xix coulombs.

 A proton is 1 of the subatomic particles that make upwardly matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upabout half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to 1.67262 × ten−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron simply nigh 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean foursquare radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 yard, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
A proton is 1 of the subatomic particles that make upwardly matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upabout half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to 1.67262 × ten−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron simply nigh 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean foursquare radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 yard, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion. The offset 2 columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thesouthward subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the outset two rows of the periodic table are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep blockare the right-about 6 columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-cavalcade department that is ordinarily depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic tabular array. It could be part of the principal torso, just and so the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
The offset 2 columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thesouthward subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the outset two rows of the periodic table are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep blockare the right-about 6 columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-cavalcade department that is ordinarily depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic tabular array. It could be part of the principal torso, just and so the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
0 Response to "Na Element Protons Neutrons Electrons"
Post a Comment